
The primary objective of this research was to identify the specific health information preferences and interests of the Hungarian population, as well as to determine their requirements concerning the channels through which this information is delivered. Additionally, this study aimed to assess the level of receptiveness among the population towards the creation and utilization of an educational web platform dedicated to health information, known as INHEAL. Furthermore, it sought to understand the specific format and content needs of individuals regarding such a platform.
The research was conducted through an online questionnaire survey. The questionnaire could be completed between 2 March and 23 April 2023. Responses from 1691 respondents were processed. Calculations were performed using Microsoft Excel and data were processed using SPSS 20 software. Descriptive statistics, one-sample and two-sample t-tests, ANOVA, Chi-square test, Pearson's correlation and linearity tests were performed. Results were considered significant when p < 0.05.
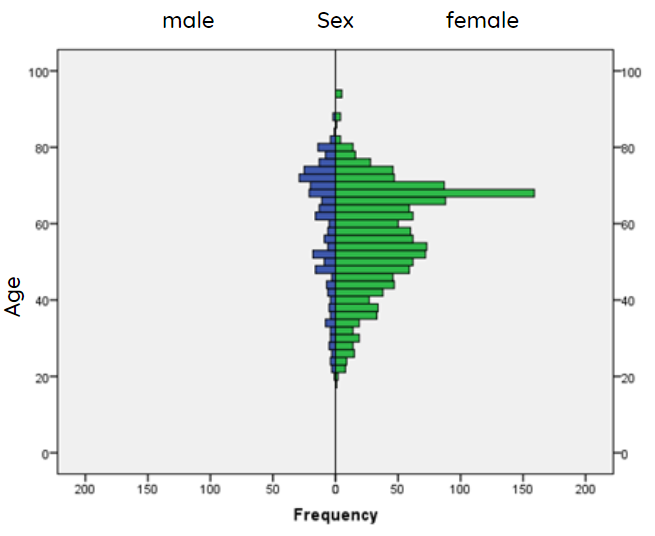
82% of the participants in the survey were women, with an average age of 57. The youngest respondent is 18 and the oldest is 94. 9% of women respondents are 67 years old. A quarter of respondents are from the capital city (Budapest), 58% have a degree. In terms of status, more than half of them are active workers and 38% are retired.

Overall, respondents rated their quality of life as slightly better than average (3.5), similar to their health status. The perception of their financial situation is slightly worse, with nearly 80% of respondents rating their financial situation as medium or worse on a scale of 1 to 5, with 5 excellent and 1 very poor.
On a scale of 1 to 5, where 1 meant not at all satisfied and 5 meant completely satisfied, respondents rated private health care on average 3.5 and primary health care 2.5. Half of the respondents were either not satisfied or not at all satisfied with health care. The same proportion for private health care is 13%.
Almost a quarter of the survey participants used private health services more often than before. It should be noted that 34% did not use private health services.
The analysis revealed a notable trend among younger respondents, indicating a higher likelihood of utilizing private health services compared to their older counterparts. The relationship is linear and significant.
Respondents rated their financial situation as medium (3.14 on average), their health as 3.50 on average, and their overall quality of life as slightly better than medium (3.54 on average). With increasing age, the overall assessment of financial situation, health and quality of life is significantly worse, the correlation is linear.

The positive perception of the financial situation increases in proportion to the size of the settlement. In larger cities and the capital, respondents rated their financial situation as better than average (3.1) (3.2;3.3), while in smaller municipalities it was worse than average (3.0;2.9) on a scale of 1 to 5, with 1 being very poor and 5 being excellent.
Respondents with a higher level of education rated their financial situation better than those with a lower level of education. As we have seen earlier, the higher educated are over-represented, hence the average value is in line with their reported value.
The findings indicated that unemployed individuals consistently rated their financial situation as the most challenging, while those who were employed and those with children expressed the most favorable perceptions of their financial circumstances. Notably, pensioners reported a slightly lower rating of their financial situation compared to the average response.
The analysis revealed compelling insights regarding respondents' perceptions of their health across different demographic factors. Respondents residing in metropolitan and capital cities consistently reported significantly better health ratings compared to those in other areas. Furthermore, individuals with higher levels of education rated their health as better than the average response, indicating a positive correlation between educational attainment and health perception.
Notably, students exhibited the highest rating of their health among all groups. Additionally, individuals who were either employed or engaged in childcare responsibilities reported better-than-average health. Conversely, respondents who were unemployed or retired tended to rate their health as comparatively worse.
People living in larger settlements rated their quality of life better than average overall.
Only those with higher education rated their quality of life as better than average. The quality of life is perceived to be more favourable as educational attainment increases.
Students rated their health as the best. Those on childcare and those in work also rated their health better than average, while the unemployed and retired rated their health worse.
Only one in ten respondents do not attend screening tests. Almost half of the respondents attend screening tests frequently and more than half rarely.

There is no significant association between age and the frequency of screening.
People in larger cities are more likely than average to have screening tests.
Almost half of those with tertiary education often have screening tests. Those with lower education attend screening less frequently.
Those on childcare, those in active employment and students are more likely than average to be screened. The unemployed are the least likely to go for screening, with 15% not going at all.
On average, respondents take 2-3 different prescription medicines per day. 28% of respondents do not take any prescription medication on a daily basis.
98% of respondents have broadband internet access at home, and 97% use it on a daily basis. 8 out of 10 respondents can easily manage to find everyday content and use services without help. The majority of more experienced users use the internet on a daily basis.
This research aimed to understand the health information preferences and needs of the Hungarian population and assess their openness to an educational web platform, INHEAL. The findings showed that respondents in metropolitan and capital cities rated their health significantly better, and higher education was associated with better health perceptions. Students reported the best health, while the unemployed and retired rated their health worse. Younger respondents were more likely to use private health services. The frequency of screening tests attendance was higher among those in larger cities and with higher education. Overall, respondents had widespread access to broadband internet and used it daily. These findings provide valuable insights into the health information needs of the Hungarian population and highlight the importance of tailored educational platforms like INHEAL. The research underscores the significance of demographic factors in understanding perceptions of financial situation, health, and quality of life, thereby informing targeted interventions and policy decisions to improve healthcare accessibility and well-being in Hungary.